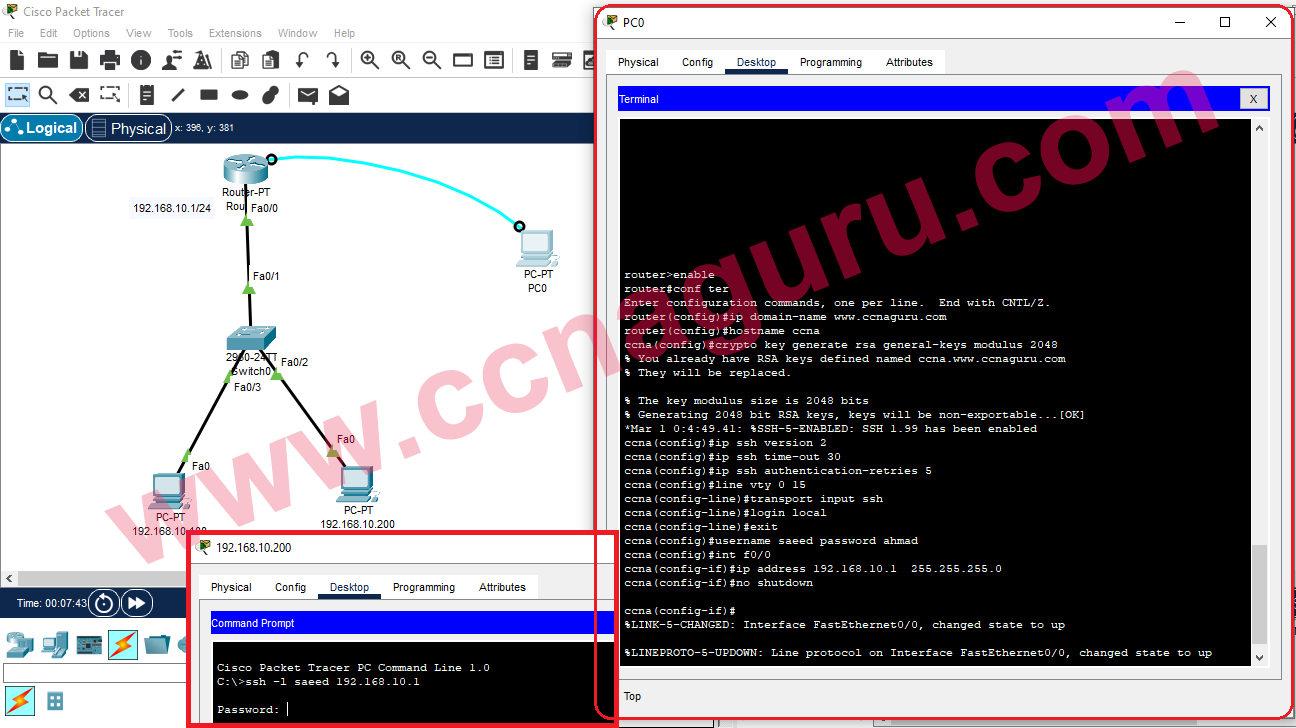
In today's digital landscape, securing remote SSH access is crucial for protecting sensitive data and maintaining system integrity. As more organizations embrace remote work, ensuring secure access to servers via SSH has become a top priority. Without proper security measures, SSH connections can become vulnerable to cyber threats such as brute-force attacks, unauthorized access, and data breaches.
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a cryptographic network protocol used to securely operate network services over an unsecured network. It provides a secure channel for remote communication between users and servers. However, as its usage grows, so does the need for robust security practices to safeguard against potential vulnerabilities.
This article delves into the importance of securing remote SSH access, offering practical strategies and best practices to enhance cybersecurity. Whether you're an IT professional or a system administrator, understanding these measures can significantly reduce the risk of cyberattacks and protect your organization's assets.
Read also:Desiremovies Bollywood Your Ultimate Guide To The Best Of Indian Cinema
Table of Contents
- Introduction to SSH
- Why Secure SSH?
- Common SSH Attacks
- Securing SSH Basics
- Advanced SSH Security
- Monitoring and Logging
- Firewall and Network Security
- Best Practices for SSH
- Tools for SSH Security
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to SSH
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a protocol designed to provide secure communication between two systems over an unsecured network. Developed in 1995 as a replacement for less secure protocols like Telnet and rsh, SSH has become the standard for remote server access. It ensures data confidentiality, integrity, and authentication through encryption.
SSH operates on a client-server model, where a client initiates a connection to a server. The protocol supports various authentication methods, including password-based and public key-based authentication. Additionally, SSH can be used for tunneling, forwarding TCP ports, and X11 connections, making it a versatile tool for remote administration.
For organizations relying on remote work, SSH is indispensable. However, its widespread use also makes it a target for cybercriminals, necessitating stringent security measures to safeguard against potential threats.
Why Secure SSH?
Securing remote SSH access is vital for maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of your systems. Without proper security protocols, SSH can become a gateway for malicious actors to infiltrate your network. Here are some reasons why securing SSH is critical:
- Prevent Unauthorized Access: Protect your systems from unauthorized users who may attempt to gain access through SSH.
- Protect Sensitive Data: Ensure that sensitive information transmitted over SSH remains confidential and cannot be intercepted.
- Enhance System Integrity: Secure SSH practices help maintain the integrity of your systems, preventing unauthorized modifications or deletions.
- Compliance Requirements: Many industries have regulatory requirements that mandate secure SSH configurations to protect sensitive data.
By implementing robust security measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of cyberattacks and protect your organization's assets.
Common SSH Attacks
Cybercriminals employ various tactics to exploit vulnerabilities in SSH configurations. Understanding these common SSH attacks is the first step in defending against them:
Read also:Kylie Jenner As A Kid The Journey Of A Young Icon
- Brute-Force Attacks: Attackers attempt to guess passwords by systematically trying different combinations until they succeed.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks: Attackers intercept and alter communication between the client and server, potentially gaining access to sensitive information.
- Keylogger Attacks: Malicious software captures keystrokes, allowing attackers to steal login credentials.
- Configuration Vulnerabilities: Misconfigured SSH settings, such as using default ports or weak passwords, can expose systems to attacks.
Staying informed about these threats enables you to implement proactive security measures to mitigate risks.
Securing SSH Basics
Update SSH
Keeping your SSH software up to date is essential for addressing known vulnerabilities and ensuring the latest security patches are applied. Regular updates also provide new features and improvements that enhance overall system performance.
Use the following command to update SSH on a Linux system:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade openssh-server
Disable Root Login
Disabling root login is a fundamental security practice that prevents attackers from directly targeting the root account. Instead, users should log in with a regular account and use privilege escalation tools like sudo when necessary.
To disable root login, edit the SSH configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Set the following parameter:
PermitRootLogin no
Restart the SSH service to apply changes:
sudo systemctl restart ssh
Advanced SSH Security
Use Key-Based Authentication
Key-based authentication is a more secure alternative to password-based authentication. It uses public and private keys to establish trust between the client and server, eliminating the need for passwords.
To set up key-based authentication:
- Generate a key pair using the
ssh-keygencommand. - Copy the public key to the server using the
ssh-copy-idcommand. - Disable password authentication in the SSH configuration file:
PasswordAuthentication no
Change Default Port
Changing the default SSH port (22) is an effective way to deter automated attacks that target this port. While it won't stop determined attackers, it can reduce the number of brute-force attempts.
Edit the SSH configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Set a new port number:
Port 2222
Restart the SSH service:
sudo systemctl restart ssh
Monitoring and Logging
Monitoring SSH activity and maintaining detailed logs are crucial for detecting and responding to potential security incidents. Regularly reviewing logs can help identify suspicious behavior and unauthorized access attempts.
Use tools like fail2ban to automatically block IP addresses that exhibit malicious behavior. Additionally, configure your system to send log alerts to administrators for prompt action.
Firewall and Network Security
Implementing firewall rules and network security measures adds an extra layer of protection to your SSH configuration. Restricting access to specific IP addresses or subnets can prevent unauthorized users from connecting to your server.
Use tools like ufw (Uncomplicated Firewall) to manage firewall rules:
sudo ufw allow 2222/tcp
sudo ufw enable
Best Practices for SSH
Adopting best practices for SSH security ensures a comprehensive approach to protecting your systems. Consider the following recommendations:
- Regularly update and patch SSH software.
- Use strong, unique passwords and enable multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Limit the number of login attempts to prevent brute-force attacks.
- Implement IP whitelisting to restrict access to trusted networks.
- Regularly audit SSH configurations and logs for anomalies.
Tools for SSH Security
Several tools can assist in enhancing SSH security:
- Fail2Ban: Automatically blocks IP addresses exhibiting malicious behavior.
- DenyHosts: Prevents SSH brute-force attacks by monitoring failed login attempts.
- SSHGuard: Protects against brute-force attacks by analyzing log files and blocking offending IPs.
- Auditd: Provides detailed logging and monitoring capabilities for SSH activity.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Securing remote SSH access is a critical component of maintaining robust cybersecurity. By implementing the strategies and best practices outlined in this article, you can significantly reduce the risk of cyberattacks and protect your organization's assets. Remember to regularly review and update your SSH configurations to address emerging threats.
We encourage you to take the following actions:
- Review your current SSH configuration and identify areas for improvement.
- Implement key-based authentication and disable password-based login.
- Monitor SSH activity and maintain detailed logs for incident detection.
- Explore additional tools and resources to enhance your SSH security.
Feel free to leave a comment or share this article with others who may benefit from these insights. For more information on cybersecurity best practices, explore our other resources and stay informed about the latest developments in the field.