South Indian languages are an integral part of the vibrant cultural mosaic that defines the southern region of India. These languages not only serve as a medium of communication but also carry the rich heritage and traditions of their respective communities. The diversity of South Indian languages is a testament to the region's deep-rooted history and cultural evolution.
India is home to a multitude of languages, and the southern part of the country boasts a particularly rich linguistic landscape. Each language spoken in this region has its own unique script, grammar, and vocabulary, making them distinct from one another. This diversity is a reflection of the region's complex history, where various dynasties and cultures have left their mark.
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of South Indian languages, exploring their origins, characteristics, and significance in modern times. Whether you're a linguistics enthusiast or simply curious about the cultural richness of South India, this guide will provide you with valuable insights and a deeper understanding of these remarkable languages.
Read also:Hdhub4uin Movie Your Ultimate Destination For Highquality Films
Table of Contents
- Introduction to South Indian Languages
- Major South Indian Languages
- Historical Evolution of South Indian Languages
- Scripts Used in South Indian Languages
- Dialects and Variations
- Cultural Impact of South Indian Languages
- Modern Usage of South Indian Languages
- Role of South Indian Languages in Education
- South Indian Languages in Technology
- The Future of South Indian Languages
Introduction to South Indian Languages
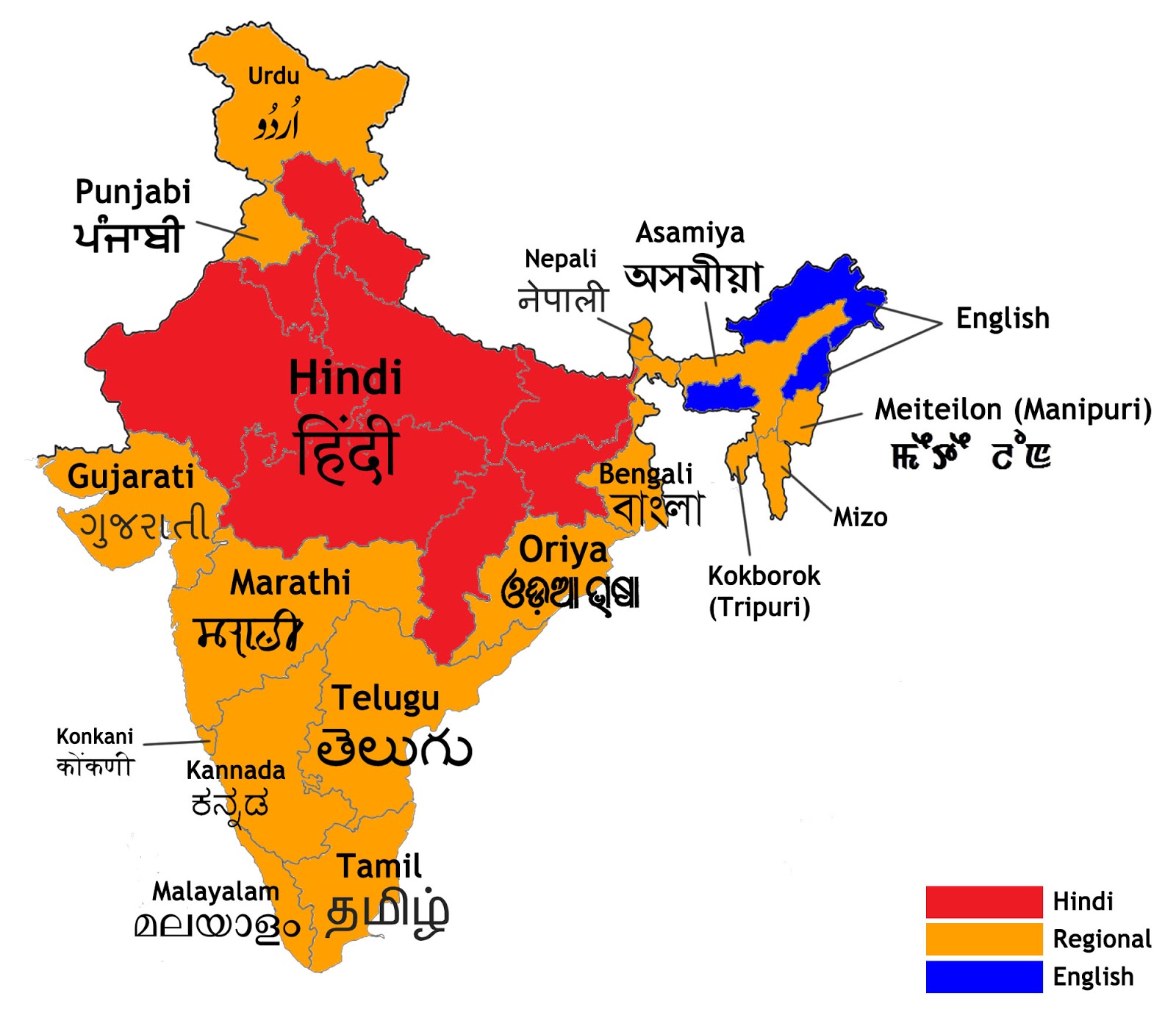
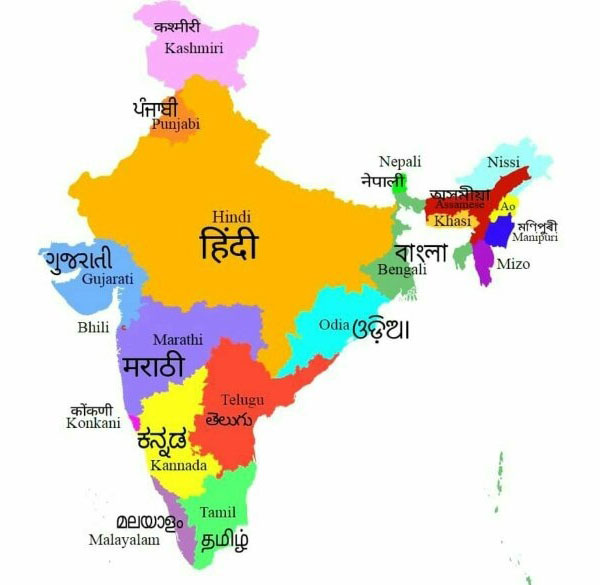
The southern part of India is linguistically diverse, with several languages spoken across the states of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana. These languages belong to the Dravidian family, which is distinct from the Indo-Aryan languages spoken in the northern part of the country. The prominence of South Indian languages is not just limited to the region; they have a significant presence globally, especially among the Indian diaspora.
Dravidian Language Family
The Dravidian language family is one of the oldest linguistic groups in the world, with a history that dates back thousands of years. It includes major languages such as Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, and Malayalam, each with its own unique features. The Dravidian languages are characterized by their agglutinative nature, where words are formed by combining morphemes.
Regional Importance
In South India, language plays a crucial role in shaping regional identity. Each state takes pride in its language, and efforts are continuously made to preserve and promote linguistic heritage. This regional pride has contributed to the flourishing of literature, cinema, and other cultural expressions in South Indian languages.
Major South Indian Languages
South India is home to several major languages, each with its own script, grammar, and cultural significance. Below is a detailed look at the most prominent South Indian languages:
Read also:Hdhub4u Download All Bollywood Movies Your Ultimate Guide
- Tamil: One of the oldest living languages in the world, Tamil is the official language of Tamil Nadu and a classical language recognized by the Indian government.
- Telugu: Known as the "Italian of the East," Telugu is the official language of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, and it boasts a rich literary tradition.
- Kannada: The official language of Karnataka, Kannada has a unique script and a long history of contributions to literature and art.
- Malayalam: Spoken predominantly in Kerala, Malayalam is known for its distinct script and a vibrant film industry.
Lesser-Known Languages
Besides the major languages, there are several lesser-known South Indian languages such as Tulu, Konkani, and Kodava. These languages, though spoken by smaller communities, are equally important in preserving the cultural diversity of the region.
Historical Evolution of South Indian Languages
The history of South Indian languages is as fascinating as the languages themselves. They have evolved over centuries, influenced by various factors such as trade, conquests, and cultural exchanges.
Ancient Origins
Archaeological evidence suggests that the Dravidian languages have been spoken in South India for at least 4,000 years. Inscriptions found in Tamil Nadu and Karnataka provide valuable insights into the early forms of these languages.
Medieval Developments
During the medieval period, the Dravidian languages underwent significant changes due to the influence of Sanskrit and Persian. This period saw the emergence of classical literature in Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, and Malayalam.
Scripts Used in South Indian Languages
Each South Indian language has its own unique script, which plays a vital role in its identity. These scripts are not only used for writing but also have cultural and religious significance.
- Tamil Script: Known for its simplicity and elegance, the Tamil script is one of the oldest writing systems in the world.
- Telugu Script: Characterized by its rounded shapes, the Telugu script is often described as the "Italian of the East."
- Kannada Script: The Kannada script is similar to Telugu but has distinct features that set it apart.
- Malayalam Script: The Malayalam script is known for its complex characters and is used exclusively in Kerala.
Dialects and Variations
South Indian languages are not monolithic; they have numerous dialects and variations that reflect the diversity of the region. These dialects are often influenced by geography, social class, and historical factors.
Regional Dialects
In Tamil Nadu, for example, there are several regional dialects such as Kongu Tamil, Madurai Tamil, and Salem Tamil. Similarly, Telugu has variations like Rayalaseema Telugu and Coastal Telugu.
Social Dialects
Social factors such as caste and occupation also play a role in shaping dialects. For instance, certain communities in Kerala have their own distinct ways of speaking Malayalam.
Cultural Impact of South Indian Languages
South Indian languages have had a profound impact on the culture of the region. They are the medium through which literature, music, and cinema are expressed, and they play a crucial role in preserving traditional knowledge and practices.
Literature
South Indian languages have a rich literary tradition, with works dating back thousands of years. Tamil literature, in particular, is renowned for its ancient Sangam poetry and epics like the Silappatikaram.
Cinema
The film industries of Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, and Malayalam are among the largest in the world. These industries produce films that are not only popular in India but also have a global audience.
Modern Usage of South Indian Languages
In modern times, South Indian languages continue to thrive, both in traditional and digital spaces. They are widely used in education, media, and technology, ensuring their relevance in the 21st century.
Education
South Indian languages are the primary medium of instruction in schools and colleges across the region. Efforts are being made to incorporate them into higher education and research.
Role of South Indian Languages in Education
The education system in South India places a strong emphasis on the use of regional languages. This approach not only helps students understand concepts better but also fosters a sense of cultural pride.
Challenges
Despite their prominence, South Indian languages face challenges such as the dominance of English and the need for standardized teaching materials. However, initiatives are being taken to address these issues.
South Indian Languages in Technology
The digital age has opened new avenues for the use of South Indian languages. From mobile apps to social media platforms, these languages are increasingly being integrated into technology.
Language Technologies
Advancements in natural language processing and machine translation have made it possible to use South Indian languages in various technological applications. This has improved accessibility and inclusivity in the digital space.
The Future of South Indian Languages
The future of South Indian languages looks promising, thanks to ongoing efforts to preserve and promote them. These efforts include language documentation, revitalization programs, and the use of technology to reach wider audiences.
Global Recognition
As the world becomes more interconnected, South Indian languages are gaining global recognition. This recognition is not only limited to academia but also extends to popular culture and media.
Conclusion
In conclusion, South Indian languages are a testament to the rich cultural heritage of the region. They have evolved over thousands of years, adapting to changing times while retaining their unique characteristics. The diversity and vibrancy of these languages make them an invaluable part of India's linguistic landscape.
We invite you to explore further by reading related articles on our website. Feel free to leave a comment or share this article with others who might find it interesting. Together, we can celebrate and preserve the linguistic treasures of South India for future generations.